Advantages of research proposals
advertisement

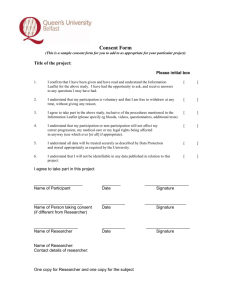
1 RESEARCH PROPOSAL Department Library and Information Science Table of Contents 2 Introduction: Definition of Research: Definition of proposal: What is Research Proposal? Objective/Purpose of the research proposal: Types of research proposal: Elements of research proposal: Cont… 3 Modules of a Research Proposal: Advantages of research proposals: Limitations and Delimitations Evaluating the Research Proposal: Why proposals fail? Conclusion: References: Introduction 4 A document that is typically written by a Researcher or scientist which describes the ideas for an investigation on a certain topic. A research proposal is a document written by a researcher that provides a detailed description of the proposed program. The presentation of an idea that you wish to pursue Definition of Research 5 According to Oxford Dictionary: “The systematic investigation into and study of materials and sources in order to establish facts and reach new conclusions.” Burns(1997:2) defines: “A systematic investigation to find answers to a problem” Definition of proposal: 6 “the act of offering or suggesting something for acceptance, adoption, or performance” (dictionary.reference.com) “an act of putting forward or stating something for consideration” (merriam-webster.com) What is Research Proposal? 7 According to Uma Sekaran: “A document that sets out the purpose of the study and the research design details of the investigation to be carried out by the researcher.” (Sekaran, 2006) According to William G Zikmund: “A written statement of the research design that includes a statement explaining the purpose of a study and a detailed systematic outline of a particular research methodology” (Zikmund, 2000) Objective/Purpose of the research proposal: 8 Objective is a way of detailing the purpose of a study. Objectives are set by the researcher to explain in detail what the study is expected to achieve To present the research question to be researched and relate its importance. To discuss the research efforts of others who have worked on related research questions. To suggest the data necessary for solving the research question and how the data will be gathered, treated and interpreted. To present the researcher's plan, services and credentials in the best possible way to encourage the proposal's selection over competitors. To help the researcher to define the contents and to plan and execute his/her research project. To inform potential collaborators and supporters about the topic and the expected quality of the research. Types of research proposal: 9 There are two types of research proposal Internal Proposal External Proposal Solicited Proposal Unsolicited Proposal (Cooper, 1995) Elements of research proposal: 10 Title Abstract Problem Statement Research Question Hypothesis Literature Review Methodology and research methods Field work Duration Final Product Budget Appendices Structure/ Modules of a Research Proposal: 11 Executive Summary Research Objectives Problem Statement Literature Review Importance of the Study Research Design Data Analysis Nature and Forms of results (Cooper, 2006) Cont… 12 Qualifications of Researcher Budget Schedule Facilities and special Resources Project Management Bibliography Appendices Advantages of research proposals: 13 Advantages to researchers Planning and Review of steps Guideline of the Investigation A Review of Previous Plans Controlling Errors Estimation of Cost Estimation of Time Advantages: 14 Advantages to the Sponsor/Supervisor Selection of the researcher Checking the sincerity of the researcher Knowledge of the Researcher Display of Researcher's Discipline Comparison of Research Proposal with Project Limitations and Delimitations 15 Limitations Limitations are the shortcomings, conditions or influences that cannot be controlled by the researcher that place restrictions on your methodology and conclusions. Any limitations that might influence the results should be mentioned. Your analysis. The nature of self-reporting. The instruments you utilized. The sample. Time constraints. Limitations and Delimitations …Cont 16 Delimitations Delimitations are choices made by the researcher which should be mentioned. They describe the boundaries that you have set for the study. This is the place to explain: The things that you are not doing (and why you have chosen not to do them). The literature you will not review (and why not). The population you are not studying (and why not). The methodological procedures you will not use (and why you will not use them). Evaluating the Research Proposal: 17 Proposal must be neatly written in appropriate writing style Major topics should be easily found and logically organized. Proposal must meet specific guidelines set by the sponsor. Technical writing style must be clearly understood and explained. Justify the chosen research project. Describe the current state of knowledge on the research topic, considering important relevant literature. Formulate the hypothesis or research questions. Define the research strategy and methodology to be used to test the hypothesis. Discuss ethical considerations about the research methodology. Serve as an important tool for monitoring the research. Checklist Creteria for Approving authorities 18 1. Is the proposal problem solving? 2. Is the problem important? 3. Is this the appropriate foundation? 4. Is the proposal innovative? 5. Will the project become self-supporting? 6. Can the proposing group do the work? 7. Is the project demonstrative (i.e., can it be used as a model)? 8. How will the program be evaluated? 9. Is the amount of money requested sufficient? Why proposals fail? 19 Basically, there are three major reasons why research proposals fail. Ethics clearance Failure to follow guidelines Reviewer concern Why proposals fail? 20 There are also some Problems which cause the Failure of Research Proposal Improper presentation of proposal Unorganized proposal Not clear written Language problem Background problem statement Not according with client's thinking Extraneous detail of literature review Not understandable Schedule and budget not mentioned Time frame not mentioned Reference 21 Books; Cooper, Donald R., C. William Emory, (1995) Business Research Methods, 5th ed. Mc-Graw Hill International Edition, , ch.4 & 18 Sekaran, Uma. (2006) “Research Methods for business” 5th ed. John Willey, New Delhi. Pp. 47-50 Zikmund, William G. (2000) “Business research method” 6th ed. Dryden, New York. Pp. 92 Cooper, Donal R., Pamela S. Schindler, Business Research Methods, 9th ed. Mc-Graw Hill International Edition, 2006, ch. 4& 21 Other Sources; http://www.scribd.com/doc/27892872/Research-Proposal www.nrf.ac.za/yenza/research/proposal.htm www.wikipedia.com http://www.webguru.neu.edu/undergraduate-research/research-funding/research-proposals http://user.spring8.or.jp/?p=672&lang=en#ch01 http://www.writeawriting.com/academic-writing/research-project-proposal/ http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/proposal http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/proposal