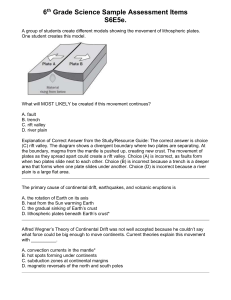
File - Mr. Fox`s Science Centre
advertisement
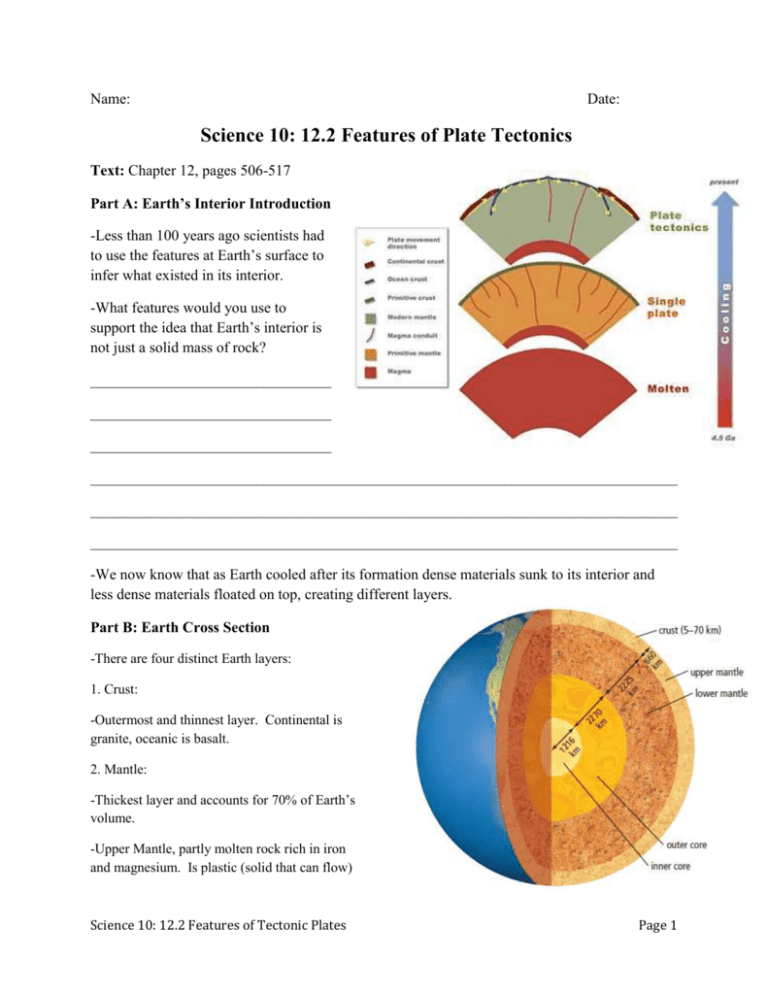
Name: Date: Science 10: 12.2 Features of Plate Tectonics Text: Chapter 12, pages 506-517 Part A: Earth’s Interior Introduction -Less than 100 years ago scientists had to use the features at Earth’s surface to infer what existed in its interior. -What features would you use to support the idea that Earth’s interior is not just a solid mass of rock? ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ -We now know that as Earth cooled after its formation dense materials sunk to its interior and less dense materials floated on top, creating different layers. Part B: Earth Cross Section -There are four distinct Earth layers: 1. Crust: -Outermost and thinnest layer. Continental is granite, oceanic is basalt. 2. Mantle: -Thickest layer and accounts for 70% of Earth’s volume. -Upper Mantle, partly molten rock rich in iron and magnesium. Is plastic (solid that can flow) Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 1 -Lower Mantle: Solid, dense and rich in iron and magnesium. 3. Outer Core: -Liquid, made of iron and nickel. 4. Inner Core: -Earth’s centre. Made of mostly iron and some nickel. High pressure makes it solid despite hot temperatures (5000 to 6000 °C). Part C: Tectonic Plates -There are about 12 tectonic plates and they can be composed of two types of materials. What are they? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ -The upper portions of the mantle and crust can further be subdivided into two separate layers: 1. Asthenosphere: ___________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ 2. Lithosphere: __________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ -Two which of the layers above do the tectonic plates belong? _____________________________________________________________________________________ Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 2 Part D: Tectonic Plate Motion -Where do you think the heat that keeps the asthenosphere molten is coming from? ______________________________ ______________________________ -Explain how the addition of heat to the asthenosphere generates convection currents. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ -Convection currents are one of the driving forces behind the movement of tectonic plates. Other contributing factors include: 1. Ridge Push: _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ 2. Mantle Drag: _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Slab Pull: _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 3 Part E: Tectonic Plate Interactions -Plate boundaries are where two tectonic plates interact. There are three main types: 1. Divergent -What type of plate movement is occurring here? ___________________________________________________ -Rift valleys become mid-ocean ridges given enough time. -Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the longest mountain chain in the world. Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 4 2. Convergent What type of plate movement occurs here? _____________________________________________________________________________________ -Type of convergent boundary depends on the composition of the colliding plates: a) Oceanic-Continental Plate Convergences -Which of the two plates colliding here would subduct? Why? _____________________________________________________________________________________ -What features are formed by this type of plate interaction? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 5 b) Oceanic-Oceanic Plate Convergences -If both plates are made of the same material (basalt), why does one subduct? _____________________________________________________________________________________ -What type of features will be formed? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ c) Continental-Continental Plate Convergences -When two continents collide, why does one plate not subduct? _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ -What type of features form from this collision? _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 6 3. Transform -How is this plate boundary different from the others we have looked at? __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ -What features would be produced by this type of interaction? __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ *Below is a summary of plate tectonic interactions: Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 7 Part F: Earthquakes 1. Earthquake Formation -Friction between interacting plates can create stress (the build-up of pressure). -When the stress gets too great the plates slip and release the stored energy. -What is the difference between the Focus (Hypocentre) and Epicentre? ________________________________ _______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ -Examine the map right. Where would the deepest focus be found? ______________________________ ______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ -What depth of Earthquake do you think will cause the most damage? Why? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 8 2. Seismic Waves -Energy released from earthquakes travels outwards from the focus as waves. There are three types: -Seismic waves have been very useful to scientists in revealing the nature of Earth’s interior. For example, seismic waves speed up as they descend into the mantle, which indicates that the mantle’s density is increasing with depth. Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 9 3. Measuring Earthquakes -Seismometers measure the amount of ground motion, the time of earthquake and how long it lasted. -Earthquakes are measured by magnitude, with a 10x increase in magnitude between numbers on the Richter Scale. -How much stronger is a magnitude 9 earthquake than a magnitude 5? __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ *Try 12-2C: Interpreting Seismograms Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 10 Part G: Volcanoes -The movement of tectonic plates cause three main types of volcanoes: Composite, Shield and Rift. -With a partner, you will select one volcano type and research a specific volcano of that type (You will need to get this approved by Mr. Fox). You will create a small presentation that must cover the following points: 1. Name and location of your volcano. 2. Type of tectonic plate boundary your volcano is associated with. You should discuss the nature of this boundary. 3. Discuss your volcanoes distinguishing features. 4. Relate the type of plate boundary and magma/lava created to the shape/characteristics of your volcano (if applicable). *Make sure that you take your own notes on all three volcano types from the text! Science 10: 12.2 Features of Tectonic Plates Page 11