File - My Grammar Garden Tutorials
advertisement

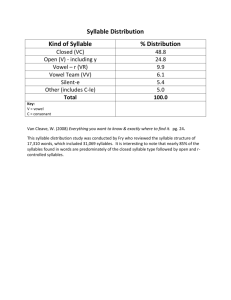
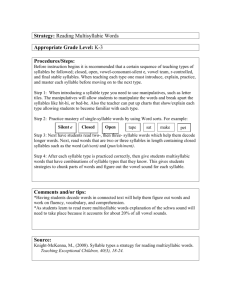
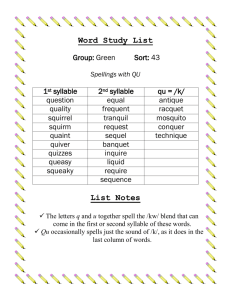
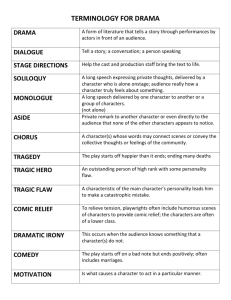
Stress in Languages – The Rhythm of the Language Rhythm generally means a “movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions.” It is “a regular recurrence or pattern in time.” Stress – Timed Languages Stressed syllables occur at a roughly constant rate. The stress is like the beat in music. Non-stressed syllables are shortened to accommodate this. The pattern of stressed and non-stressed syllables is like the rhythm of music. Non-stressed syllables have a vowel, which is the Schwa. Every vowel can become a schwa if it is in an unstressed syllable. Syllable – Timed Language Japanese - is quite different from European and some Asian languages. Each syllable is pronounced with equal length. Japanese sounds like a steadily flowing stream. German – the accent is generally on the first syllable, except for prefixes: be/ ge / er / emp / ent / ver / zer Italian French IPA Symbols – primary stress is indicated by a high vertical line before the syllable. English Dictionaries – show stress by placing a prime mark after the stressed syllable. Fixed Stress – can usually be predicted by a rule. Examples: Hungarian, Icelandic. Variable Stress – is less predictable and must be memorized as part of the pronunciation of the word. Examples: English, Russian, Italian, Spanish British English – lab OR a tor y / American English – LAB or a tor y Word or Lexical Stress – stress accent is placed on syllables. Sentence or Prosodic Stress – stress is placed on words in a sentence or phrase. Contrastive Stress – is used to highlight an item that is given particular focus.