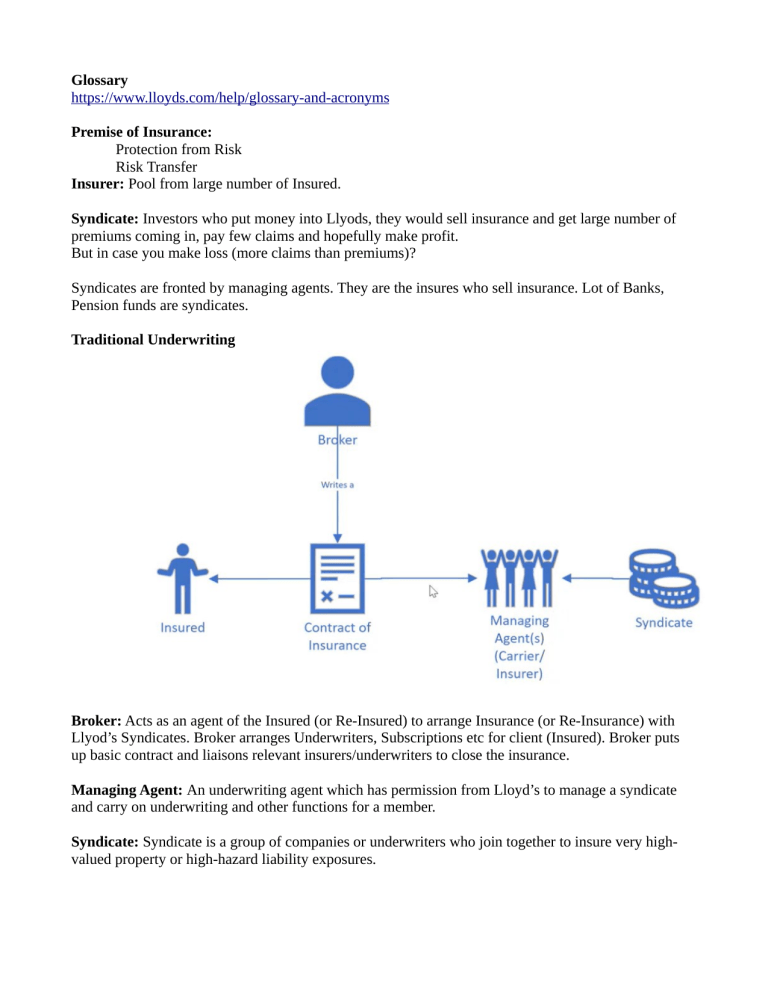
Glossary https://www.lloyds.com/help/glossary-and-acronyms Premise of Insurance: Protection from Risk Risk Transfer Insurer: Pool from large number of Insured. Syndicate: Investors who put money into Llyods, they would sell insurance and get large number of premiums coming in, pay few claims and hopefully make profit. But in case you make loss (more claims than premiums)? Syndicates are fronted by managing agents. They are the insures who sell insurance. Lot of Banks, Pension funds are syndicates. Traditional Underwriting Broker: Acts as an agent of the Insured (or Re-Insured) to arrange Insurance (or Re-Insurance) with Llyod’s Syndicates. Broker arranges Underwriters, Subscriptions etc for client (Insured). Broker puts up basic contract and liaisons relevant insurers/underwriters to close the insurance. Managing Agent: An underwriting agent which has permission from Lloyd’s to manage a syndicate and carry on underwriting and other functions for a member. Syndicate: Syndicate is a group of companies or underwriters who join together to insure very highvalued property or high-hazard liability exposures. Llyod’s: Corporation which regulates and provides support services to the market. It’s not an Insurance company, rather a society of individuals and corporate underwriting memnbers that insure and reinsure risks as member of one or more syndicates. If you are a Managing agent or Broker of Llyods, you get regulated by Llyods through auditing etc. Why London market populare? Because it has got Llyod’s. Lloyd’s has got very high reputation of paying claims. If syndicate fails to settle, Lloyd has the guarantee to settle the claim. It has solvency regulations on syndicates by ensuring their business plans to be robust by several measures including re-insurance. Subscription Market: Each insurer taking a chunk of the Risk. Example: a ship worth 10 Million whose risk is distributed among 10 insurers for 1 million each. Layers / Reinsurance: Insurer may take an insurance on the possible underwriting loss in return for a premium. Reinsurance accounts for more than half the Lloyd’s total business. Horizontal Vs Vertical Layers: Horizontal: 10 Million sliced into 10 chunks of 1 Million each. Vertical: 1st Insurer wil pay any claims upto 5 Million, then next insurer will pay (between 5 and 10 Million). Risk Spread: Syndicates spread the risk by diversifying their insurances. Example: A syndicate insures a huge number of properties in Texas (which has a high risk of storm). It also insures electrical sub stations in another part of the world. So the chances of natural disaster occurring in both places is really small. Insurance Platform: More standardized products are traded through e-platforms such as acturis, Global XB, Novidea etc, but not used very much in London Market, because of it’s complexity, redundancy and non-standard approach of dealing. A lot of communication happens through emails and face to face. PPL and Whitespace are two leading platforms in London. Generally brokers goes to trade with a dozen clients with a mix of Risks (low, medium, high) as a bundle/package and offer to give it as a bundle to underwriters. High end Special Commercial Insurance: Standard Insurance: Example, car insurance are pretty standardized and can be completely executed by technology/online without broker intervention. With the advent of technology, broker industry has been squeezed. Risk pertaining to small commercials (shops, offices etc) can be packaged without broker and the commission is so minuscule that if you are deploying a broker, you are making a loss. Gradually, with technology and AI, more and more insurance will be transformed to packaged products. On the contrary, there are few spaces which are difficult to automate. Role of Broker: A broker (ideally) works for Insured/Client, not for the Insurer. Broker commission should come from customer’s payment. But in reality it could be different. The commission percentage is often set by the Insurer. Ideally a broker should work for the Insured. Broker should not work for the Insurer and present the best insurance to the client and not the one that pays the best commission. There are Audit mechanism that questions broker the basis of it’s sell (of insurance) to client to ensure that client is presented with the best value. In other hand, involvement of Broker is some times necessary to get the best Insurance at the best price in the market among many competitors (Insurers). Delegated Underwriting: Managing agent will have to do a lot of activities to set up the contract, hence it’s administratively heavy. For a risk such as a Vessel, on accord of years of experience, Insurers can develop a product which is well defined for a specific size, specification of a Vessel and specific Risk, the premium is say X amount. This can be set up as a product that can be sold by somebody else. That somebody is called a Cover Holder. It’s similar to a Wholesaler-Retailer mode. Cover Holder: A managing agent may delegate to another company, including to a Lloyd’s broker, its authority to enter into contracts of insurance on behalf of a syndicate it manages. The recipient of the authority is known as a ‘coverholder’. Cover holder sends monthly statement, which is called bordeaux, to the Insurer. Bordeaux: A list of premiums payable and claims paid or due which is prepared by a coverholder for a managing agent or by a reassured for its reinsurer. Bordereaux are commonly produced on a monthly or quarterly basis. They breakdown block premium payments that are made to underwriters and detail claim payments made on behalf of or due from underwriters. The bordeaux is a way to deal with volumes. Rather than having each individual transactions (Insurances, Premiums, Claims etc) which could be in thousands in case of a really good product, is delegated to Cover holders by the Insurer. This delegations are seen in small commercials, large commercials. US Market: Even though it’s the biggest market in the world, north American property insurance, they don’t have adequate underwriters, so it often comes to London. Licensed agents in US act as cover holders for London Insurers/brokers. But for large Risks, produced in US are placed in London. There could be many parties involved such as local broker in New York, who would probably place some risk in local NY Insurers while taking bigger chunks to London broker. There could be chain of brokers, Advisors and Specialists etc involved. That’s an example of Wholesale market which involves real money with series of comission. Sections: A Risk is divided into sections. Each section may depend on business classification (A section that covers all buildings of a Business, another section covers all stocks, another section covers employees etc). A section may be defined based on Geography or Vicinity. Another example could be a division based on mode of payment. Everything that’s paid in USD could be a section and those paid in Sterling could be a different section. Or it could be combination of various criteria/division. They way sections are defined could be very simple to very arbitrary. Section is generally defined by Broker. Each section is attached to one or more Insurer. Hierarchy: Contract → Section → Insurer (1 → N) CDR(Core Data Record): The Core Data Record is a set of Standardized, Quality Transactional data, that empowers downstream processing. The CDR holds the critical transactional data required to be captured at written line across four downstream processes: • premium validation and settlement • claims matching at first notification of loss • tax validation and reporting, and • regulatory validation and core reporting. For more understanding, visit this link Core Data Record (CDR) | Blueprint Two (velonetic.co.uk) CDR is not live at this moment, but in future it’s going to be the defacto standard or structure for creating an Insurance electronically. LIMOSS(London Insurance Market Operations & Strategic Sourcing): Is a service company for Llyod’s. They provide first line support for Lloyd’s systems in terms of Market Services for London Market to deliver high quality service and value for money. LIMOSS | Overview ACORD(Association for Cooperative Operations Research and Development): Is the Global standardsetting body for Insurance and related financial services industries. It facilitates fast, accurate data exchange and efficient workflows through the development of electronic standards, standardized form and tools to support their use. ACORD is the messaging standard which connects Market Services. It provides structure of the data being exchanged. LIMOSS | ACORD ACORD Reference Architecture: Provides an enterprise architecture framework for the insurance industry. It has following components which can be utilized collectively or individually. ACORD Reference Architecture



