Week 5
advertisement

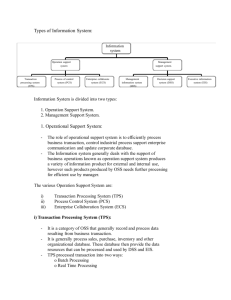
Business Systems: Electronic Commerce, Transaction Processing Systems (TPS), Management Information Systems (MIS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Decision Support System (DSS), Group Decision Support System (GDSS), Executive Support System (ESS/EIS) Chapter 5 and 6 Electronic Commerce History Began in the early 1970s innovations such as electronic transfer of funds (EFT) were limited to large corporations and a few daring small businesses Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) added other kinds of transaction processing and extended the types of participating companies ANSI X.12 standardized in 1983 EDIFACT standardized in 1986-87 Over the last five years innovative applications, from advertisement to auctions and procurement fueled by the internet Types of Electronic Commerce Business-to-consumer EC (B2C) companies sell directly to consumers over the Internet Business-to-business EC (B2B) two (or more) businesses make transactions electronically More than $7.3 trillion volume by 2004 15x volume of B2C Mostly done by EDI – 95% of EC is EDI! Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) E.g. E-bay, Classifieds Government-to-citizens (G2C) and to others Doing taxes online etc. Mobile commerce (m-commerce) Wireless commerce. E.g. Using cell phone to pay for gas Supply Chain Management Value Chains in E-Commerce Conversion to e-commerce supply chain management provides businesses with an opportunity to: increase revenues or decrease costs by eliminating time-consuming and labor-intensive steps throughout the order and delivery process improve customer satisfaction by enabling customers to view detailed information about delivery dates and order status reduce inventory including raw materials, safety stocks, and finished goods Product and Information Flow for HP Printers Ordered Over the Web E-Commerce Applications Retail and Wholesale Cybermall Electronic exchange Manufacturing Marketing Investment and Finance On-line Stock Trading On-line Banking Electronic Retailing Solo storefronts Examples: walmart.com, buy.com Can use services like http://store.yahoo.com Cybermalls Stores give up some freedom to be part of the mall Some solo stores expand to become malls Amazon.com, Buy.com Some malls are more like intelligent agents for comparing prices (pricegrabber.com) Companies can both be in a mall and a solo storefront Issues in E-tailing Channel conflict Lego.com: Keeping consumers and retailers happy (very small percent of revenue from online sales) Order fulfillment Shipping small quantities to many customers. How to handle returns? B2B E-commerce Sell-side marketspaces One company trying to sell its goods to many companies Customized catalogs, auctions Buy-Side marketspaces / E-procurement One large buyer, many smaller suppliers Examples: Supermarket chains, Ford, Boeing Alternative: Group procurement (e.g. shop2gether.com) Electronic Exchanges Many sellers and many buyers An Electronic Exchange Key Technical Components •Catalog Management •Product Configuration •Shopping Cart •E-commerce Transaction Processing •Web Site Data Analysis •Linux •Unix •Windows Electronic Payment Systems •Credit cards, smart cards •Digital certificate •Electronic cash •Electronic wallet •P2P payment (PayPal) Decision: Develop or outsource? •Apache Web server •Oracle •Web construction •PC •Mainframe •Mid-range Transaction Processing Information Systems What is a transaction? Grocerystore purchase, airline ticket reservation, deposit money to an account. Something is exchanged (money, goods, ...) What data is collected? What transactions did you take part in yesterday? Transaction Processing major business processes provide the mission-critical activities transaction may generate additional transaction Transaction Processing System (TPS) computerized information system supports the transaction processes Critical to the well-being of the organization!! Characteristics of TPS Large amounts of data are processed The TPS processes information on a regular basis High level of detail in data Low complexity of calculations Systems must be very reliable Large storage (database) capacity is required Need lots of processing speed due to the high volume Input and output data are structured Need high level of accuracy, data integrity, and security Must allow for queries of data Transaction Processing Overview Transaction Processing Systems Batch Processing System Transactions are accumulated over time and processed in a single group On-line Transaction Processing (OLTP) Each transaction is processed immediately Examples? Does anyone use a batch processing system? Know of one? Heard of one? TPS, MIS/DSS, and AI/ES Transaction Processing Activities Data Collection Source data automation makes it easier Data Editing Check for validity and completeness Data Correction Re-enter invalid data Data Manipulation Simple calculations Data Storage Update databases Document Production Business documents and Reports Example: Point-of-Sale System Order Processing Systems Systems that process order entry, sales configuration, shipment planning, shipment execution, inventory control, invoicing, customer interaction, and routing and scheduling Integration of TPSs Management Information Systems Provide routine information to managers in the functional areas Provide information in exception reports and ad hoc (demand) reports Terminology Originally: ’MIS’ used for everything having to do with IT and IS Today: ’MIS’ used for this type of system (except in a few universities!) MIS gets input from TPS Management Information System Sources of Managerial Information Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Provide real-time monitoring of business functions Permits timely analysis of issues such as quality, availability, customer satisfaction, performance, and profitability. Combines TPS and MIS (among other things) Advantages Elimination of costly, inflexible legacy systems Improvement of work processes Increase in access to data for operational decision making Upgrade of technology infrastructure Disadvantages Expense and Time in Implementation Difficulty Implementing Change Difficulty Integrating with Other Systems Risks in Using One Vendor Decision Support Systems Support for Problem-Solving Phases Different Decision Frequencies One-time: ad hoc DSS Repetitive: Institutional DSS Different Problem Structures Highly structued vs. Semi or unstructured Support for Various Decision-Making Levels Operational, tactical, strategic Decision Making Level Book, p. 238 Model of a DSS •Financial Models •Statistical Analysis Models •Graphical Models •Project Management Models Group Decision Support System Software application that consists of most elements in a DSS, plus software needed to provide effective support in a group decision making Special design Ease of use Flexibility Decision-making support Anonymous input Reduction of negative group behavior Parallel communication Automated record keeping GDSS Configuration GDSS Alternatives Executive Support System Tailored to individual executives Easy to use Drill down capabilities Support need for external data Can help when uncertainty is high Future-oriented Linked to value-added processes Support for defining an overall vision strategic planning strategic organizing and staffing strategic control crisis management Next Week Thanksgiving December 4 Lecture Chapter 8 Group Presentations Team 4, 5 and 6